Views: 3 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-01 Origin: Site
The properties of refractory materials are very important. They can handle high heat, strong chemicals, and heavy weight. They also do not break when temperatures change quickly. You use refractory bricks in places with a lot of heat. Regular bricks cannot survive in these places. These bricks keep furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces safe. They are strong and last a long time. Their special materials and how they are made help them stay strong. They do not get damaged as easily as normal bricks.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Resistance | Can handle very high heat above 1000°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Does not get damaged by acids, bases, or slags |
| Mechanical Strength | Can take a lot of rubbing and heavy weight |
| Low Porosity & High Density | Stops harmful things and lasts longer |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Does not crack when temperature changes fast |
| Dimensional Stability | Keeps its shape and size even under stress |
Refractory bricks can handle very high heat, strong chemicals, and heavy weight. This makes them good for furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces.
Fire bricks are not like regular bricks because they can take much higher heat. They also last longer and do not crack or break easily.
When picking refractory materials, look at thermal resistance, chemical stability, mechanical strength, and low heat loss.
The right refractory bricks help save energy, protect equipment, and lower repair costs at work or at home.
Always follow safety rules and use a checklist to choose the best refractory bricks. This keeps your equipment and your team safe.

Refractory bricks are used when things get very hot. They do not lose their shape or strength, even above 1000°C. These bricks are made from materials like alumina, silica, and magnesia. Sometimes, they also have silicon carbide. This mix helps them stand up to heat and chemicals from gases or melted metals.
Refractory bricks do not crack or break easily. They can be heated and cooled many times. This is called thermal shock resistance. Many factories use these bricks in furnaces and kilns. Industries like steel, glass, and ceramics need them. Yufeng Refractory bricks have a lot of alumina. This makes them last longer and work well under stress.
Here are some important things about refractory bricks:
They keep their shape and size when hot.
They can handle quick changes in heat.
Chemicals do not damage them.
They help save energy by holding in heat.
They last a long time, even in hard places.
Their tiny structure, like porosity and alumina, makes them strong.
Fire bricks are not the same as regular bricks. Fire bricks, or refractory fire bricks, have a special job. They can take much higher heat than regular bricks.
| Aspect | Fire Bricks (Refractory Fire Bricks) | Regular Bricks |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumina, silica, magnesia, silicon carbide, sometimes graphite or chromite | Clay, shale, and other natural minerals with impurities |
| Manufacturing Process | Fired at 1300-2000+ °C, strict control of raw materials | Fired at 900-1100 °C |
| Temperature Resistance | Can handle 1580-2000+ °C, keep strength at high temperature | Safe below 800 °C, lose strength above 600 °C |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High, can handle many cycles of heating and cooling | Low, cracks after repeated heating |
| Durability | Very high, lasts long in harsh environments | Lower, breaks down faster under stress |
You pick fire bricks for fireplaces, kilns, or furnaces. Regular bricks are good for walls and buildings. But they cannot handle high heat. Fire bricks do not wear out, corrode, or crack easily. They keep your equipment safe and working well.
When you pick materials for hot places, you must know the key properties of refractory. These properties help you choose bricks that last longer and save energy. They also keep your equipment safe. Here are the most important things to remember.
Thermal resistance means refractory can stand high heat without melting or breaking. You need this when you use bricks in furnaces or kilns. Not all bricks can take the same heat. Some bricks are for normal jobs. Others are for tough or super tough jobs.
Here is a table that shows how much heat different refractory bricks can take before they fail:
| Brick Type | Maximum Temperature Before Structural Failure | Supporting Evidence Summary |
|---|---|---|
| High Alumina Bricks | ~1400°C | Stay strong up to ~1250°C; get weak above 1400°C and start to fail. |
| Andalusite Bricks | ~1100°C | Change from brittle to bendy at 900°C; lose strength above 1100°C; no strength at 1500°C. |
| Fused Silica Bricks | >1500°C (retain strength) | Act brittle above 1100°C but stay strong up to 1500°C. |
| High Alumina Cement Castable | >1500°C (retain strength) | Change to bendy above 1100°C; stay strong up to 1500°C. |
Super tough bricks like fused silica and high alumina cement castable can take the most heat. Tough bricks like high alumina bricks are strong but get weak above 1400°C. Always check the brick’s heat rating before you use it.
Let’s look at how different refractory materials handle heat:
| Material Type | Thermal Resistance (Max Temp °C) | Thermal Shock Resistance | Chemical Stability | Notes on Thermal Properties and Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Bricks | >1750 | High | Good in acidic/neutral environments | Good heat resistance, strong, and not too expensive |
| Fireclay Bricks | ~1400-1500 | Lower than alumina | Moderate | Good for medium heat, not as strong with heat changes |
| Silica Bricks | ~1650 | Lower than alumina (prone to cracking) | Good against acidic slags | High heat resistance but crack easier |
| Magnesia Bricks | >2000 | Good but chemically limited | Best in basic slag environments | Can take more heat but not good with all chemicals |
| Carbon Bricks | Very high (no melting) | Excellent thermal conductivity | Vulnerable to oxidation | Great heat resistance but not good in air |
| Zirconia Bricks | ~2200 | Exceptional | Very stable | Highest heat resistance but very costly |
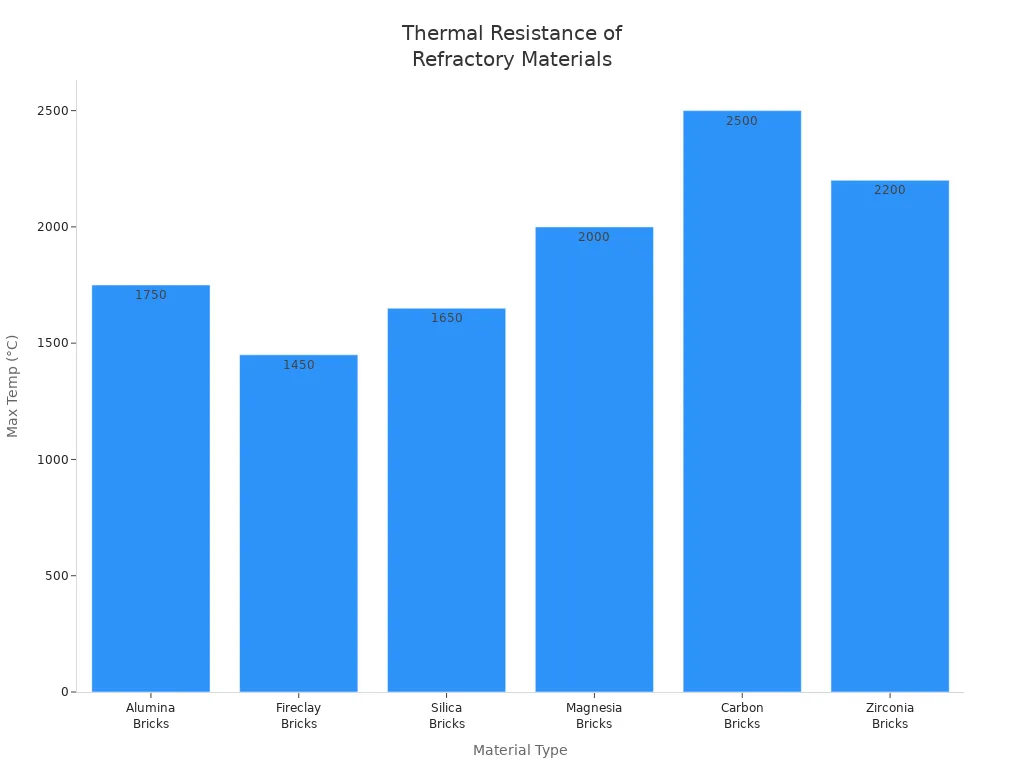
Tip: Always match the heat resistance of your refractory bricks to the hottest temperature your equipment will reach. Using the wrong brick can make it break early and cost you money.
Chemical stability means refractory bricks can fight off damage from chemicals like acids and alkalis. Many factories have harsh chemicals. If bricks react with these, they break down faster.
Here is a table that shows which refractory bricks resist different chemicals:
| Type of Refractory Brick | Main Chemical Resistance | Typical Chemical Compounds Resistant To | Industrial Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silica Bricks | Acidic slags | Acidic chemical compounds (e.g., acidic slags) | Coke ovens, glass furnaces |
| Magnesia Bricks | Basic slags | Basic chemical compounds (e.g., basic slags, alkalis) | Steelmaking, rotary kilns, converters |
| Aluminosilicate Bricks | Alkaline silicate melts | Alkaline chemical compounds (alkaline silicate melts) | High-temperature environments |
Acid resistant refractory can handle acids like sulfuric acid.
Alkali resistant refractory, like magnesia bricks, stand up to alkalis.
Phosphate-bonded refractory can fight both acids and alkalis.
The chemical stability of refractory depends on what it is made of and how many tiny holes it has. Bricks with fewer holes fight chemicals better. For example, andalusite bricks have fewer holes, so they resist alkalis well.
Chemical stability is tested by seeing how well bricks fight off chemicals at high heat. If you use bricks with poor chemical stability, they wear out faster and need to be replaced more often.
Note: Always pick refractory bricks that match the chemicals in your process. This helps your equipment last longer and saves you money on repairs.
Mechanical strength means refractory bricks can take heavy loads and hits. You need strong bricks in places with lots of pressure or movement, like furnace floors.
Here is a table that shows how strong different refractory bricks are:
| Grade | Cold Crushing Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| FLG135-1.20 | 10 |
| FLG130-1.30 | 20 |
| FLG130-0.8 | 2.2 |
Good refractory bricks can be as strong as 20 MPa or more. Some super tough bricks can be even stronger. Stronger bricks crack and chip less from use.
Loading or moving can cause cracks and chips.
Heat changes also wear down bricks.
Strong bricks last longer and protect your equipment.
Experts say making refractory bricks stronger helps them last longer in tough places. Adding special stuff like graphitic carbon can make bricks denser and stronger.
Tip: Always check how strong your refractory bricks are, especially for tough jobs. Stronger bricks mean less downtime and lower repair costs.
Low thermal conductivity means refractory bricks do not let heat escape easily. This helps save energy in furnaces and kilns. Bricks with low thermal conductivity keep more heat inside and lose less to the outside.
Here is a table that shows how much heat different refractory bricks let through:
| Refractory Brick Type | Thermal Conductivity Range (W/(m·K)) | Notes on Temperature Effect and Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Brick | ~14.28 to 15.35 | Lets the most heat through, not much change with temperature |
| Alumina-Carbon Composite Brick | ~10.63 | Lets some heat through, less as temperature goes up |
| Corundum Brick | ~5.92 | Lets the least heat through, less as temperature goes up |
Low thermal conductivity means less heat lost through walls and floors.
You save energy because you need less fuel to keep things hot.
The bricks help keep the inside temperature steady and protect your equipment.
Note: If you want to save energy and spend less, pick refractory bricks with low thermal conductivity. This is very important in places like steel and glass factories.

Refractory bricks are used in many big furnaces. These bricks protect furnace walls from very high heat. They also stop damage from strong chemicals. Steel plants use them in ladles and blast furnaces. Cement factories put them in rotary kilns and coolers. Glass makers use them in tank furnaces and regenerators. Power plants need them in burner blocks and ash hoppers. Petrochemical refineries use them in reformers and gasifiers.
Refractory bricks have special features for these jobs. They can take high heat for a long time. They do not get ruined by acids or alkalis. They are strong and can handle heavy loads and movement. You pick different bricks for each part of the furnace. Magnesia bricks are good for basic slag areas. Silica bricks work best in places with acids.
Tip: Always choose bricks that match the furnace’s heat and chemical needs. This keeps things safer and makes bricks last longer.
Refractory bricks are important in kilns and fireplaces. You see them in ceramic kilns and pottery ovens. Glass furnaces also use these bricks. Fire clay bricks and high alumina bricks line kilns to handle high heat. Insulating fire bricks help keep heat inside and save energy. In fireplaces and pizza ovens, these bricks stop cracks and keep heat steady.
Here is a table that shows brick types and their uses:
| Type | Key Component | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fire clay bricks | Alumina + Silica | Ceramic kilns, fireplaces |
| High alumina bricks | High alumina content | Steel furnaces, rotary kilns |
| Silica bricks | Quartz (Silica) | Glass furnaces, coke ovens |
| Magnesia bricks | Magnesium oxide | Cement rotary kilns |
| Insulating fire bricks | Lightweight alumina | Kiln linings |
You pick bricks based on how hot the kiln gets and what you are firing. Insulating bricks help save fuel and keep the kiln’s heat steady.
Steelmaking and blast furnaces need the strongest bricks. High-alumina bricks are used where it gets up to 1770°C. These bricks do not get ruined by slag or melted metal. They also stand up to hits and fast heat changes. Refractory bricks make a strong wall that protects the furnace. This keeps the furnace safe and saves energy.
Using the right bricks stops erosion and cracks. Good bricks help the furnace lining last longer and cost less to fix. They also help make better steel because the furnace stays steady.
Note: Picking the right bricks for steelmaking and blast furnaces saves money, keeps workers safe, and helps things run better.
Picking the right refractory keeps your equipment safe. You need to match the refractory brick to your job. Use this checklist to help you choose:
Define your application: Know what you want the refractory to do. Think about if it is for a furnace, kiln, or fireplace.
Check temperature resistance: Make sure the material can take the highest heat your equipment will reach.
Assess chemical resistance: Pick a refractory that does not get ruined by acids, alkalis, or slags.
Evaluate mechanical strength: Choose materials that can handle heavy weight, rubbing, and hits.
Consider thermal shock resistance: If your equipment heats and cools fast, pick a refractory that does not crack.
Review installation method: Decide if you need bricks, castables, plastics, or gunning materials. Some ways work better for certain shapes or repairs.
Check size and fit: Make sure the refractory fits your space and matches your design.
Balance cost and quality: Look at the price, but also think about how long the material will last and how much fixing it needs.
Plan for maintenance: Pick materials that are easy to check and fix.
Consult experts: Ask professionals if you are not sure what you need.
Tip: Always match the refractory to the hottest temperature and strongest chemicals in your process. This helps stop early damage and keeps your work safe.
You can make things safer and work better by following these tips:
Wear safety gear like gloves, goggles, and dust masks when you handle refractory.
Work in a clean, dry place with good air flow to avoid dust and water problems.
Clean and level surfaces before you install. This helps the refractory stick and last longer.
Use the right tools to cut and shape. Always follow safety rules so you do not get hurt.
Let the refractory cure and dry for the right amount of time. If you rush, it can crack or get weak.
Add expansion joints where needed. This lets the refractory grow and shrink without breaking.
Check your refractory often. Look for cracks, worn spots, or places that get too hot.
Keep notes on all repairs and checks. This helps you find problems early and plan fixes.
Teach your team how to handle and care for refractory safely.
Work with skilled installers and follow the maker’s instructions for the best results.
Note: Picking the right refractory and following safety steps protects your equipment and your team. Good care saves money and stops accidents.
Knowing about refractory material properties helps you choose well for your equipment. You should check what chemicals are in it, how dense it is, and how it was made. These things change how much heat it can take, how strong it is, and how safe it will be. Picking the right refractory keeps your team safe and your machines working. Use the checklist and safety tips to help you decide and take care of your equipment for the best results.
Refractory bricks can take much more heat than regular bricks. You use them in hot places like furnaces and kilns. Regular bricks will break or crack if they get too hot.
Check how hot your equipment gets. See what chemicals are there. Pick bricks that fit these needs. If you are not sure, ask an expert for help.
Yes! Refractory bricks keep heat inside furnaces and kilns. This means you use less fuel. Less heat escapes, so you save energy and money.
You should check refractory bricks every few months. Look for cracks, chips, or other damage. Early checks help stop bigger problems and keep things safe.
You can use refractory bricks in fireplaces and pizza ovens. They can take high heat and do not crack easily. Always follow the instructions when you install them for best results.