Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-20 Origin: Site
When you pick insulation for your home or work, safety is very important. Research says ceramic fiber insulation and glass fiber insulation are not big cancer risks for people who use or install them. Studies and safety checks did not find strong proof of serious health problems from these materials in normal use. You should still wear masks and gloves, like safety rules say. Both types can make your skin and eyes feel itchy if you do not handle them carefully. Experts also want you to think about the whole life of the insulation, because some types can let out chemicals that hurt air quality and people nearby.
Ceramic fiber insulation can take very high heat and fire. This makes it good for factories. But you must handle it carefully to stay safe and healthy.
Glass fiber insulation is safer for homes and daily use. It causes less health problems. It also breaks down faster in the body.
Always wear gloves, masks, goggles, and special clothes when using either insulation. This keeps your skin, eyes, and lungs safe.
Ceramic fiber insulation cools down fast after a fire. It does not get damaged by quick temperature changes. This helps keep workplaces safer.
Pick insulation based on what your project needs. Use ceramic fiber for places with high heat. Use glass fiber for homes or places with less heat.
Ceramic fiber insulation is great for places with high heat. Many factories use it because it can take very hot temperatures. It can handle heat up to 2600°F (1425°C). This makes it good for furnaces, boilers, and kilns. The main parts are alumina and silica. Some types have zirconia too. These fibers make a light product that is strong and bends easily.
Here is a quick look at the technical features:
| Specification Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Up to 2600°F (1425°C) |
| Composition | Alumina, silica, zirconia |
| Physical Properties | Low density, low heat storage, low thermal conductivity, fire safety |
| Product Forms | Blankets, boards, paper, modules, bulk |
| Applications | Furnace linings, boilers, pipes, storage tanks, industrial insulation |
Ceramic fiber insulation comes in many shapes. You can use a folded ceramic fiber blanket to wrap pipes or line furnaces. Boards and modules fit into walls or ceilings. Each type helps keep heat inside and protects equipment.
Tip: If you pick ceramic fiber insulation, you get great fire resistance. This material will not burn, so it helps stop fire from spreading. It does not hold much heat. When a fire ends, the insulation cools fast. This lowers the chance of burns or damage.
Ceramic fiber insulation can handle fast changes in temperature. It does not crack or break when the temperature changes quickly. This keeps your workplace safer. You do not have to worry about sudden heat causing damage.
It is easy to use ceramic fiber insulation because it is light and bends well. You can cut or shape it to fit what you need. Always wear gloves and a mask to keep your skin and lungs safe. This material does not have asbestos. You do not face the same health risks as with old insulation.
Ceramic fiber insulation helps control heat well. It keeps heat where you want it. It also protects people and equipment from burns or fire. You can trust this insulation to work safely in hard places.
Glass fiber insulation stands out as a popular choice for both homes and businesses. You will find it in attics, walls, and ceilings. This material uses fine glass strands to trap air, which slows down heat movement. You get good thermal insulation and lower energy bills.
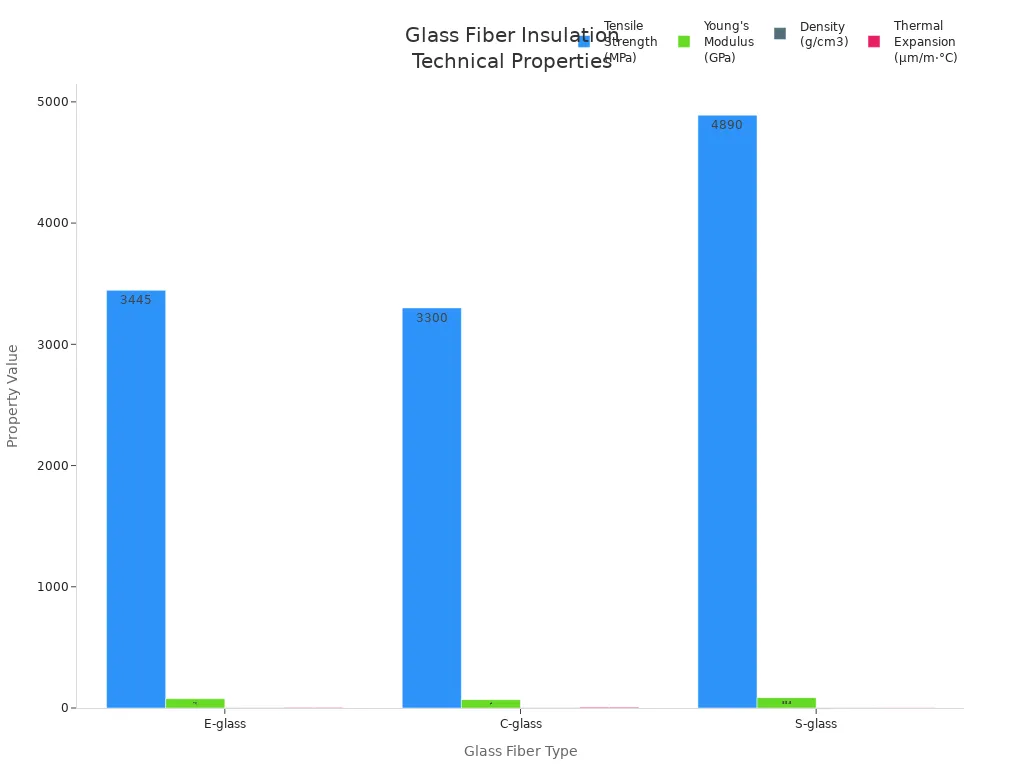
Glass fiber comes in several types. E-glass is the most common. It works well for most building needs. C-glass resists chemicals, so you see it in places with harsh environments. S-glass gives you higher strength and better temperature resistance. Each type has a unique mix of silica and other oxides.
| Characteristic | E-glass | C-glass | S-glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 (%) | ~55 | ~65 | ~65 |
| Al2O3 (%) | ~8 | ~4 | ~25 |
| CaO (%) | ~19 | ~14 | N/A |
| MgO (%) | ~4.6 | ~3 | ~10 |
| Na2O (%) | ~0.3 | ~8.5 | ~0.3 |
| Softening Point (°C) | ~846 | N/A | ~1056 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ~3445 | ~3300 | ~4890 |
| Density (g/cm³) | ~2.58 | ~2.49 | ~2.46 |
You can see how the different types compare in this chart:
When you install glass fiber insulation, you need to think about safety. Tiny fibers can irritate your skin, eyes, and lungs. You should always:
Wear gloves, long sleeves, pants, and a dust mask.
Use safety goggles to protect your eyes.
Work in a space with good airflow.
Avoid rubbing your skin if it gets itchy. Use tape to remove fibers gently.
Wash your hands and face after handling insulation.
Note: Professional installation helps keep you safe and ensures the insulation works well. If you do it yourself, follow all safety steps to avoid health problems.
Glass fiber insulation does not burn easily. It softens at high temperatures, but it will not catch fire in normal use. You get reliable protection for your home or workplace. This makes it a strong choice for many projects, especially when you compare it to older materials like asbestos or even some types of Ceramic Fiber Insulation.
It is important to know how ceramic fiber insulation and glass fiber can affect your health. Both can bother your skin, eyes, and lungs. If you touch them, your skin might itch or get red. Breathing in the fibers can make you cough or give you a sore throat.
Here is a table that lists the main health risks for each:
| Aspect | Ceramic Fiber Insulation (RCF) | Glass Fiber (MMVF) |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Symptoms | Nasal stuffiness (55%), eye and skin irritation (41%, 36%), wheeze (18%), dry cough (13%), chronic bronchitis (12%)—more common in smokers | No link to respiratory cancer or chronic lung disease at normal exposure; mild, reversible irritation possible |
| Lung Function Changes | Small decreases in lung tests, mostly in smokers; some studies show lower lung function in workers | No consistent evidence of lung problems in normal work settings |
| Pleural Changes | Pleural thickening and plaques after long exposure (over 20 years); no deep lung scarring | No known pleural or lung scarring |
| Skin and Eye Irritation | Common among workers | Mild, short-term irritation |
Note: Studies say glass fiber insulation does not cause cancer or serious lung disease for workers. Ceramic fiber insulation can cause more chest and lung problems, especially if you use it for many years or smoke.
Groups like OSHA and IARC say glass fiber is not known to cause cancer. Workers who make or use glass wool do not get more lung disease. For ceramic fiber insulation, animal tests show a higher risk of lung cancer and chest problems. People who work with ceramic fibers for a long time may cough more and have more chest changes.
You need to be careful when you work with insulation. Both ceramic fiber insulation and glass fiber can make your skin itch and your eyes water. Fiberglass can quickly make your skin itchy or give you a rash. Ceramic fiber insulation can also bother your skin, but breathing in its dust is more dangerous over time.
You should always wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with these materials. Here is what you need for ceramic fiber insulation:
Wear gloves that can handle high heat.
Use goggles to keep your eyes safe.
Put on clothes that cover your skin.
Wear a dust mask or respirator.
Handle the insulation gently so you do not break the fibers.
Make sure the insulation is held up well so it does not move or tear.
Check the insulation often to see if it is damaged.
Clean up dust and pieces after you finish.
Follow the instructions from the company that made it.
If you use glass fiber, you should also wear gloves, long sleeves, and a dust mask. Wash your hands and face when you are done. Both types need careful handling, but ceramic fiber insulation needs more care because it can cause more health problems over time.
You want insulation that keeps you safe from fire and heat. Ceramic fiber insulation is very good at stopping heat and fire. It can take much higher heat than glass fiber.
Here is a table that compares their fire and heat ratings:
| Material Type | Melting Point (°C) | Long-term Working Temp (°C) | Short-term Temp Tolerance (°C) | Fire Test Outcome Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber | 1760 | 1050 | >1300 | Kept steel wire below 300°C for 60 minutes under rapid heating to 1100°C |
| Ordinary Glass Fiber | 1200-1350 | N/A | N/A | Lower melting point; less effective alone for high-temp fire resistance |
| High Silica Glass Fiber | N/A | 1000 | 1400 (short-term) | Good for short-term high temperatures; often used with aluminum foil for extra protection |
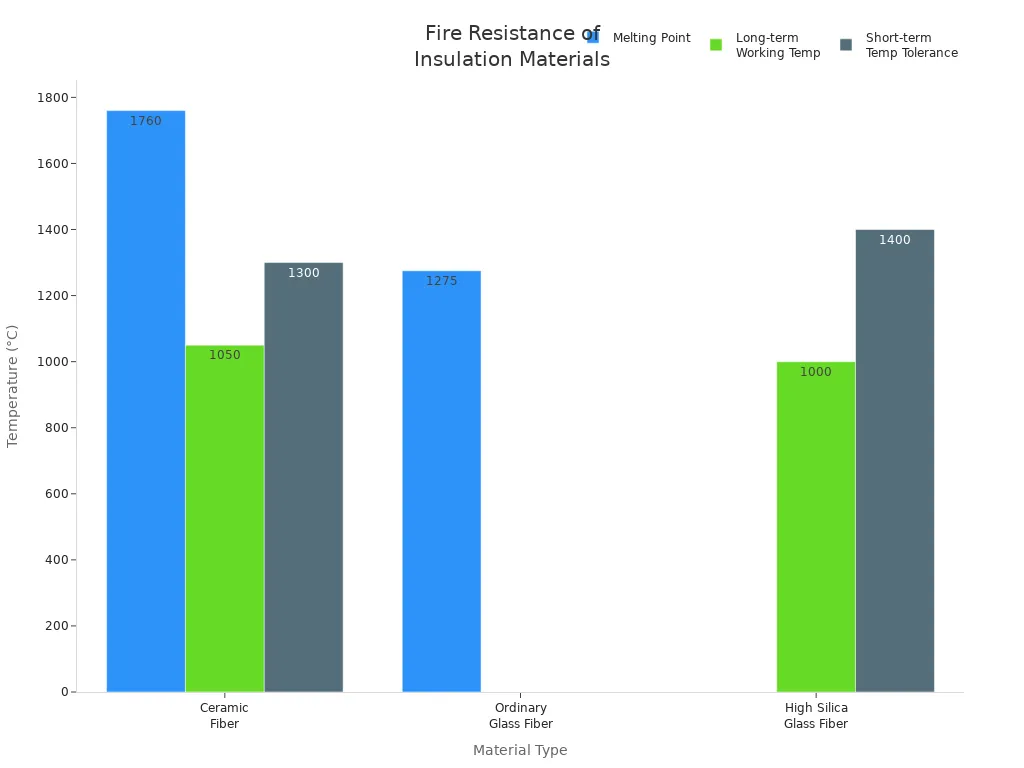
Ceramic fiber insulation does not burn or melt easily. It stays strong in fires or very hot places. Glass fiber can stop fire, but it melts at lower heat. High silica glass fiber works better than regular glass fiber in hot spots, but it still cannot beat ceramic fiber insulation for very high heat.
Fire tests show ceramic fiber insulation keeps things cooler longer during a fire. This makes it a great pick for places where fire safety is very important.
You should think about the environment when you choose insulation. Sometimes, glass fiber insulation is made from recycled glass. You can reuse or use it again in some cases, but recycling is not common because the fibers break down. Most old insulation goes to waste centers, and trained workers take it out to keep everyone safe.
Fiberglass insulation is not usually recycled, but it does not hurt the environment if you throw it away the right way.
Ceramic fiber insulation does not have special recycling rules. You need to take it to a waste center.
Neither material has asbestos, so you do not need to worry about those strict rules.
Always let trained workers take out and throw away old insulation. This keeps you and the environment safe.
Ceramic fiber insulation and glass fiber both do not change shape much when they get hot or cold. This helps them last longer and keeps buildings safe.
Factories and plants use ceramic fiber insulation and glass fiber insulation. Ceramic fiber insulation works well in places with very high heat. You see it in furnaces, kilns, and power plants. It can handle fast temperature changes. It keeps equipment safe from fire. Glass fiber insulation is used in places that do not get as hot. It is common in HVAC ducts and building insulation.
Here is a table that shows how insulation materials compare for factories:
| Insulation Material | Safety Features | Durability Characteristics | Regulatory Compliance & Standards | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber | Fire resistant, withstands extreme heat | Lightweight, resists thermal shock | Meets industrial fire safety standards | Ideal for furnaces, kilns, power plants |
| Mineral Wool | Fire resistant, withstands extreme temps | Dense, durable, moisture resistant | Aligns with strict fire safety regulations | Used in oil refineries, power stations |
| Calcium Silicate | Non-combustible, withstands high heat | High mechanical strength, chemical resistant | Complies with fire safety regulations | Suitable for steam and process piping |
| Cellular Glass | Non-combustible, fire resistant | Moisture and chemical resistant, stable over time | Meets industrial safety standards | Ideal for high-pressure steam and petrochemical use |
| Polyurethane/Polyiso Foams | Moisture resistant, energy efficient | Lightweight, resists deterioration over time | Meets UL, CSA, IEC, ISO standards | Used in refrigeration, petrochemical industries |
Safety tip: Always wear gloves, goggles, and a mask when you work with insulation. Training helps you stay safe. Wet insulation and clean with a vacuum to control dust.
Common safety problems in factories are:
Skin itching or rash
Nose, throat, and eye irritation
Breathing in dust or fibers
You can lower these risks by wearing protective gear and following safety rules.
You want your house to be warm in winter and cool in summer. Glass fiber insulation is the best choice for most homes. It is safe, cheap, and easy to buy. You can put it in attics, walls, and ceilings. Glass fiber breaks down in your body, so it is safer if you breathe in a little dust.
Ceramic fiber insulation is not used much in homes. It does not break down in your lungs. Breathing in the fibers can cause health problems. Most experts say not to use ceramic fiber insulation in houses.
When you put insulation in your home, you should:
Follow the International Building Code (IBC) and local rules.
Use insulation with the right R-value for your area.
Make sure the material meets fire safety standards like ASTM E84.
Wear gloves, long sleeves, and a dust mask.
Use vapor barriers to stop moisture problems.
Note: Glass fiber insulation is safer for homes. It meets building codes and keeps your family comfortable.
You need special insulation for places with very high heat. Ceramic fiber insulation is best because it can take temperatures up to 1430°C (2606°F). It is light, does not break easily, and keeps heat inside. You see it in furnaces, kilns, and power plants.
Glass fiber insulation cannot take very high heat. It may melt or get weak. Other materials, like mineral wool and calcium silicate, work up to 1000°C (1832°F). Microporous insulation can take even more heat but costs more.
Here is a chart that compares how much heat different insulation materials can take:
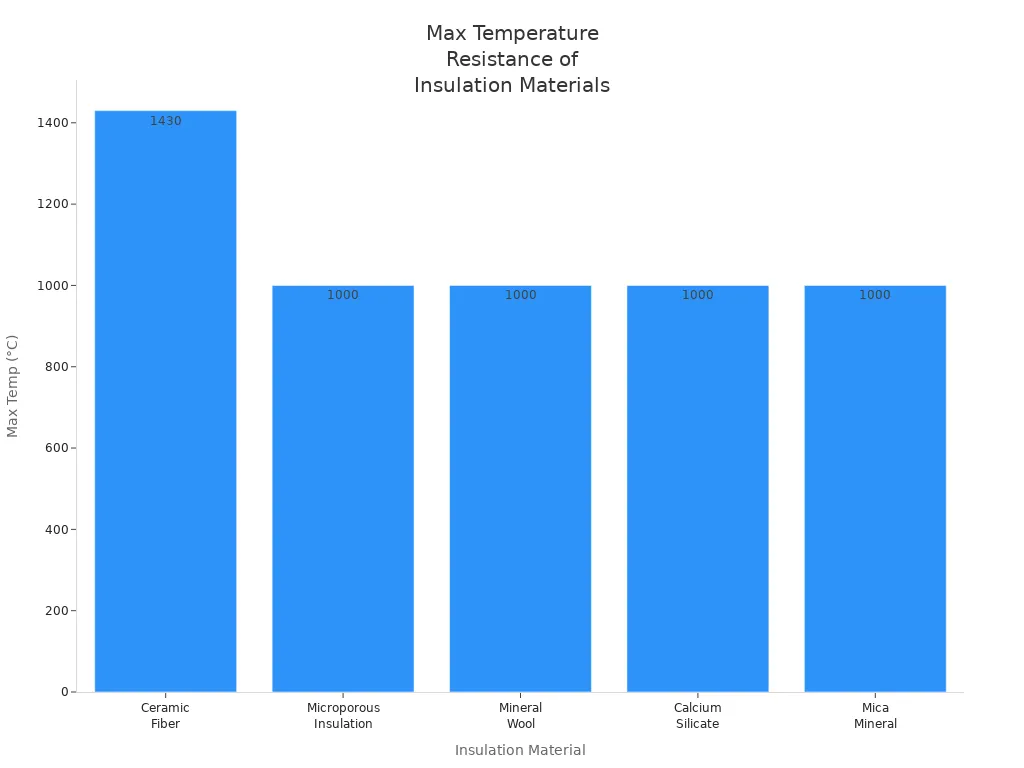
Ceramic fiber insulation gives you the best safety and performance for very hot places. You should check the insulation often for damage. Always wear protective gear when you install it.
When you look at Ceramic Fiber Insulation and Glass Fiber Insulation, you want to know which is safer. This table shows the most important safety facts for both types. It helps you choose the best insulation for your project.
| Safety Metric / Property | Ceramic Fiber Insulation (Refractory Ceramic Fibers) | Glass Fiber Insulation (Fibrous Glass Wool) |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenicity Classification | Possibly carcinogenic (IARC) | Not classifiable; some biopersistent fibers may be carcinogenic |
| Fiber Dissolution Rate | Bio-soluble or biopersistent, depends on type | Biosoluble fibers dissolve faster, biopersistent dissolve slowly |
| Maximum Use Temperature | 1350°F to 3000°F | Up to ~1200°F for textile glass insulation |
| Density (pcf) | Grades 3 to 12 | Usually lower than ceramic fiber |
| Thermal Conductivity | Up to 0.66 Btu·in/(hr·ft²·°F) at 400°F | About 0.29 Btu·in/(hr·ft²·°F) at 75°F |
| Linear Shrinkage | Specified in ASTM C 892 | Included in standards for glass fiber boards |
| Tensile Strength | Specified in ASTM C 892 | Included in standards for glass fiber boards |
| Non-fibrous (Shot) Content | Specified in ASTM C 892 | Specified in ASTM C 612 |
| Water Vapor Sorption | Measured by ASTM C1104 | Measured by ASTM C1104 |
| Wicking | Measured by ASTM C1559 | Measured by ASTM C1559 |
| Fire Resistance | High, best for fireproof applications | Fire resistant, lower max temperature |
| Health Precautions | PPE, professional installation, proper disposal | PPE, ventilation during installation |
Tip: Always use gloves, a mask, and long sleeves when you touch insulation. These protect your skin and lungs from tiny fibers.
You can see how Ceramic Fiber Insulation and Glass Fiber Insulation are different in temperature, density, and thermal conductivity in this chart:
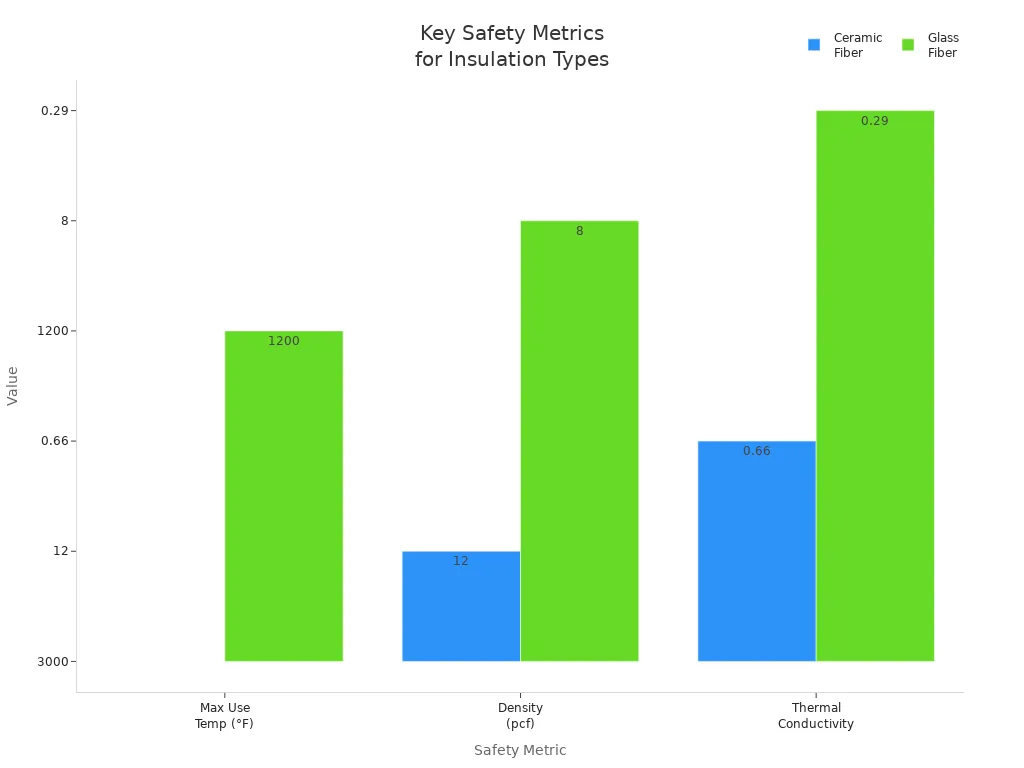
Ceramic Fiber Insulation is best for very hot places. It gives strong fire safety and does not break down with chemicals. Glass Fiber Insulation works well in homes and places that do not get too hot. Biosoluble glass fibers are safer for your health. You must wear protective gear and follow safety rules with both types.
Here are the main things to remember:
Ceramic Fiber Insulation can take very high heat and fire.
Glass Fiber Insulation is safer for health if it uses biosoluble fibers.
Both need careful handling and safe disposal.
Fire resistance and fiber type are the most important for safety.
Use the table and chart to help you decide. Pick the insulation that fits your safety needs and your project.
You can notice safety differences between ceramic fiber insulation and glass fiber. Glass fiber insulation is usually safer for homes and businesses. Health groups say it does not cause cancer. You can stop skin itching by wearing gloves and masks. Ceramic fiber insulation is better for places with very high heat. Experts say to be careful because it may cause health problems. For most jobs, glass fiber insulation is best for health, easy use, and the environment.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation can take very high heat. It does not burn or melt fast. You can use it in furnaces and kilns. This keeps workers and equipment safe in hot places.
Most homes should not use Ceramic Fiber Insulation. Breathing in the fibers can hurt your health. Glass fiber insulation is better for houses. It keeps you safer and more comfortable.
Wear gloves, a mask, and goggles. Put on long sleeves and pants. Work where air moves well. Clean up dust when you finish. These steps help stop skin and breathing problems.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation does not have asbestos. You must take it to a waste center. Recycling does not happen much. Always let trained workers remove old insulation. This helps keep the environment safe.
Some studies show it may cause cancer in animals. You can lower your risk by wearing safety gear. Follow all safety rules. Experts say glass fiber insulation is safer for homes and offices.