Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-22 Origin: Site
Thermal insulation helps stop heat from moving between things by making a barrier. You use it to keep your house warm in winter and cool in summer. Materials with low thermal conductivity slow heat from moving, so you can control the temperature inside. Studies show bad insulation can make buildings lose up to 49% of energy. If you pick the right thermal insulation, you save energy and feel more comfortable.
Thermal insulation helps stop heat from moving fast. It keeps homes warm in winter. It keeps homes cool in summer. This saves energy. It also saves money.
Insulation blocks heat from moving in three ways. It stops conduction, convection, and radiation. It uses special materials to do this.
Picking insulation with a high r-value is better. It makes heat stay out or in. It helps you feel more comfortable. It lowers your energy bills.
There are many types of insulation. Some are fiberglass, mineral wool, foam, and natural fibers. Each type works best for different places and needs.
Good insulation helps homes, factories, and vehicles. It makes people feel better. It saves money. It helps protect the environment.
If you wonder what insulation is, you want a simple answer. Insulation uses special materials to slow down heat moving between places. You can find insulation in walls, ceilings, floors, windows, and doors. In building science, insulation means using materials and designs to stop heat from moving in or out of buildings. People use insulation to help control the temperature inside homes and schools.
Insulation blocks the three main ways heat moves. These are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is when heat goes through solid things like metal or wood. Convection is when heat moves through liquids or gases, like air. Radiation is when heat travels in waves, like sunlight warming a room. Materials like cellulose, glass wool, polystyrene, and reflective barriers help slow down these ways heat moves. You can look at this chart to see how insulation helps:
| Heat Transfer Method | How Insulation Helps |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Stops heat moving through solids |
| Convection | Blocks heat moving through air or liquids |
| Radiation | Reflects or absorbs heat waves |
Insulation makes your home more comfortable. It also saves energy by keeping heat where you want it. Learning about insulation helps you see why it is important for every building.
Tip: If you touch a wall and it feels cold in winter, you may need better insulation. Good insulation keeps the inside temperature steady.
You put in insulation for many reasons. The main reason is to stop unwanted heat loss or gain. This helps keep your house warm in winter and cool in summer. Insulation lets you use less energy for heating and cooling. You save money on bills and help the environment by using less electricity or gas.
Here are the main goals of insulation:
Acts as a barrier against outdoor pollutants, allergens, and moisture
Helps regulate humidity and reduce mold risk
Ensures compliance with building codes and safety standards
Contributes to your well-being and productivity
Conserves energy by minimizing unwanted heat loss or gain
Regulates thermal systems
Improves comfort by reducing temperature changes
Insulation resists heat flow. You notice this when your home stays warm even if it is cold outside. You also feel comfortable because insulation stops big changes in temperature. You can use different types of insulation for walls, roofs, floors, windows, and doors. Sealing cracks and gaps also helps stop air from leaking in or out.
Insulation gives you many benefits. You save money, feel more comfortable, and protect your health. Insulation can also block noise, air, and vapor. Some types of insulation make buildings stronger. When you ask what insulation is, you see it does more than just keep you warm or cool. It helps make your space safer, healthier, and more energy-efficient.
If you want to know how insulation works, you need to learn about heat transfer. Heat always moves from warm places to cool places. This follows a science rule called the second law of thermodynamics. Heat moves in three main ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction happens when heat goes through solid things. If you touch a metal spoon in hot soup, your hand gets warm. Heat travels through the spoon. Insulation slows conduction by using materials that do not let heat move fast. These materials make heat move slowly between particles.
Convection is when heat moves through fluids like air or water. Warm air goes up, and cool air goes down. This makes currents. In your house, heat can get out through spaces in walls or ceilings. Insulation stops convection by trapping air in tiny pockets. This keeps air from moving around.
Radiation is heat moving in waves. You feel this when sunlight warms your skin. Radiant heat does not need to touch anything or use air. Insulation like reflective barriers helps by bouncing heat away from your home.
Note: Insulation works on all three ways heat moves. You get better results if you use materials that stop conduction, convection, and radiation together.
Here is a table to show how each way works and how insulation helps:
| Heat Transfer Method | Example | How Insulation Works |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Metal spoon in hot soup | Uses low thermal conductivity |
| Convection | Warm air rising | Traps air, blocks movement |
| Radiation | Sunlight warming skin | Reflects or absorbs heat waves |
You need good thermal insulation to control these ways heat moves. If you use the right insulation, your home stays comfy and saves energy.
Insulation materials act as blocks to heat transfer. You use them to slow or stop conduction, convection, and radiation. Each kind of insulation works in its own way.
Conduction barrier: Materials like fiberglass and spray foam have loose bonds. These bonds make it hard for heat to move through solids. You get thermal resistance because particles do not pass energy quickly.
Convection barrier: Insulation makes tight seals. When you fill cracks and gaps, you stop air from moving. This keeps warm air inside and cold air outside. You also keep out moisture and air that can hurt insulation.
Radiation barrier: Reflective insulation, like shiny aluminum foil, acts like a mirror. It bounces radiant heat away from your house. Some materials can bounce up to 90% of radiant heat. You use these in attics or walls to keep heat out in summer and inside in winter.
Tip: Using both mass insulation and radiant barriers works best. You stop all three ways heat moves and save more energy.
You measure how well insulation works by its thermal resistance. The higher the thermal resistance, the better it slows heat. People call this the r-value.
The r-value shows how well insulation stops heat flow. You use it to compare different insulation types. A higher r-value means better thermal resistance and stronger thermal insulation. You add up the r-values of each layer in a wall or roof to get the total.
For example, if a material has an r-value of 4, it loses heat at a rate of 0.25 W/(°C·m²) when there is an 18 °C difference. You want a high r-value to keep your house warm in winter and cool in summer. The r-value depends on the type, thickness, and density of the material. It also changes with temperature and age.
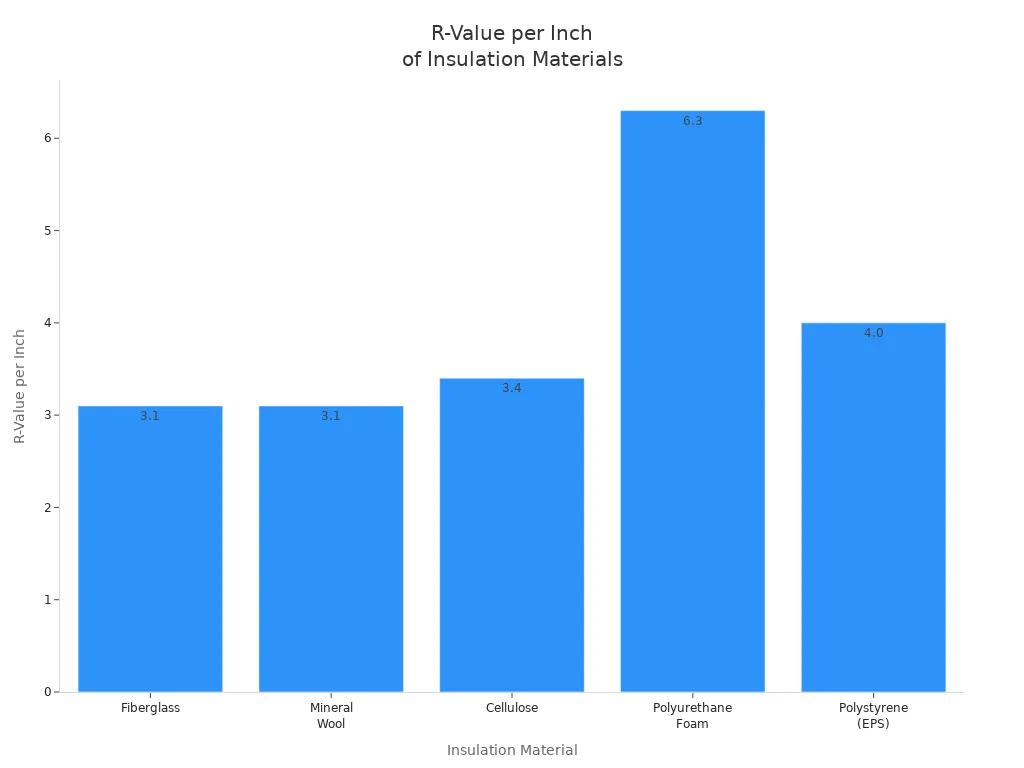
Here is a chart to help you understand r-value:
| Material | Typical R-value per inch | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass | 2.2 - 4.3 | Walls, attics |
| Spray foam | 3.5 - 6.5 | Walls, roofs |
| Mineral wool | 3.0 - 3.3 | Walls, floors |
| Cellulose | 3.2 - 3.8 | Walls, attics |
| Rigid foam board | 3.8 - 5.0 | Walls, foundations |
You need to look at the r-value when you pick insulation. If you live in a cold place, you want a higher r-value. If you live in a warm place, you may need less. The r-value helps you choose the best thermal insulation for your home.
Reminder: The r-value is important for picking insulation. You save energy and money when you choose materials with high thermal resistance.
You see the good things about thermal insulation in lower bills and better comfort. When you use insulation with a high r-value, you keep heat where you want it. You also protect your house from moisture and air leaks. You get a safer, healthier, and more energy-saving home.
There are many types of thermal insulation. Each one works in a special way. You need to pick the best one for your space.
Fiberglass is a very common insulation. It comes as batts, rolls, or loose-fill. It is made from tiny glass fibers. These fibers trap air and stop heat from moving. You use fiberglass in walls, attics, and ceilings. It blocks heat, cold, and noise. Fiberglass is cheap and easy to put in. It can last up to 20 years. You must wear safety gear when you touch it. The fibers can bother your skin and lungs. Fiberglass does not burn and resists mold. But it must stay dry or it can get wet and cause problems.
Tip: Fiberglass insulation is good for the planet. It often uses recycled glass and has a small carbon footprint.
Typical properties and uses:
R-value: 2.9–3.8 per inch
Used in homes, schools, and offices
Cuts noise and saves energy
Mineral wool includes rock wool and glass wool. You find it as batts, boards, or loose-fill. Yufeng Refractory makes strong mineral wool products. These include ceramic fiber boards and blankets. They can handle heat up to 1000°C. Mineral wool does not burn, so it is good for fireproof doors and machines. It does not soak up water, so it keeps its shape. You use mineral wool for soundproofing and thermal insulation in walls, floors, and roofs.
Key features:
R-value: about 3.1–4.0 per inch
Fire resistant and lasts a long time
Good for hot places
Foam insulation comes as spray, boards, or panels. Polyurethane, polystyrene, and polyisocyanurate are common types. Foam traps gas in tiny spaces. This makes it a good thermal insulator. You use foam in walls, roofs, and foundations. It has a high R-value, often above 5 per inch. You do not need much to get strong insulation. Foam can catch fire, so you must use fire retardants. Yufeng Refractory sells ceramic foam for industrial thermal insulation. These products are strong and resist heat.
Natural fiber insulation uses things like cellulose, hemp, flax, and sheep wool. You find it as batts, panels, or loose-fill. These types of thermal insulation come from plants or animals. They are good for the environment. You must treat them to stop pests and fire. They soak up water, which can make them work less well. Sometimes you need to replace them. Natural fibers are good for soundproofing and controlling moisture.
Advantages and disadvantages:
Good for the planet and safe for people
Can get wet or attract pests
R-value: about 3.4 per inch
Note: Air and vacuum are also good thermal insulators. Air gaps slow down heat. Vacuum panels block conduction and convection. You see vacuum insulation in special building panels. They cost more and need careful work to install.
You need to know the types of thermal insulation. This helps you pick the best one for your project. Some materials are good thermal insulators. Others are bad thermal insulators and let heat out. Always choose the type that fits your weather, budget, and safety needs.
You use thermal insulation in many places at home. You can put it in attics, walls, basements, and garages. Insulating your attic keeps heat inside in winter. It also keeps your house cooler in summer. You can use fiberglass batts, foam boards, or reflective barriers. Many people add insulation to windows and doors. They use weatherstripping, window films, or thermal curtains. These steps stop air leaks and keep the temperature steady. You might see insulation in carpet pads and water heater wraps. It can even be in playhouses or workshops. Using the right materials saves energy and lowers bills. You feel more comfortable because your home stays warm or cool.
Tip: Seal air leaks before you put in insulation. This helps you get better results and stops problems like gaps or moisture.
Factories use thermal insulation to control heat in equipment and pipes. You see it wrapped around boilers, steam lines, and tanks. Insulation keeps heat inside where it is needed. This means less energy gets wasted. Many industries use ropes, tapes, or gaskets for strong thermal barriers. This keeps machines at the right temperature. It also protects workers from burns. Insulating pipes and equipment helps heating systems work less. It saves money on energy. Good insulation can make machines last longer. It stops damage from heat and moisture. Many companies save millions by using proper insulation.
Thermal insulation is important in cars, trains, planes, and ships. In airplanes, you find it in wall panels and around engines. It is also inside air ducts. It keeps the cabin comfortable and protects parts from heat or cold. In electric cars, insulation helps control battery heat and stops fires. You also see it in trains and ships. It keeps noise down and protects against vibration. Many vehicles use foam, rubber, or special blankets. These block heat transfer and improve safety. Insulation in transportation saves energy. It also makes your ride quieter and more comfortable.
You can make your home use less energy with thermal insulation. Adding insulation keeps heat inside in winter. It also blocks heat from coming in during summer. This means heaters and air conditioners do not work as much. You save energy and money. The table below shows how insulation helps in different parts of your home:
| Aspect of Heat Loss / Insulation Impact | Documented Energy Savings / Effect |
|---|---|
| Retention of heating and cooling energy | Up to 80% of heat/cooling stays in, so you need less heating and AC |
| Heat lost through walls | About 33% of heat escapes through walls, so wall insulation is important |
| Heat lost through floors | Around 15% of heat leaves through floors, so floor insulation helps a lot |
| Heat lost through lofts and roofs | About 25% of heat goes out through roofs, so roof insulation saves energy |
| Insulating hot water tanks | You get your money back in less than a year because of energy savings |
| Overall benefits | You use less energy, pay lower bills, and help the planet |
Insulating walls, roofs, and floors gives you the biggest benefits. This keeps your home comfy and saves energy all year.
Thermal insulation helps you spend less money. You pay less for heating and cooling because your home keeps its temperature. Here are ways insulation saves you money:
You can cut your energy bills by 15-30%, saving up to $500 each year.
Spray foam insulation fills gaps, so you pay less for heating and cooling.
You spend less fixing your HVAC system because it works less.
Insulation projects pay off in about 10 years.
Homes with good insulation sell for more because buyers want energy savings.
Strong insulation lasts longer, so you save money over time.
Note: Insulation and air sealing cost about $2,100, but you save money and feel better for years.
Insulation makes your home feel better. It keeps the temperature steady, so you do not get cold spots or drafts. You also hear less noise from outside. Studies show insulation can make rooms warmer by up to 1.4°C in winter. You stay warm without turning up the heat. Insulation also keeps your home cool in summer. You breathe easier because insulation can help air quality and lower allergens. Sealing leaks and adding insulation makes every room nicer.
Steady indoor temperatures
Fewer cold spots and drafts
Less noise from outside
Cleaner air
Thermal insulation helps the environment by lowering energy use and cutting pollution. When you use less energy, you burn fewer fossil fuels. This means less carbon dioxide goes into the air. Adding insulation to many homes can cut CO2 as much as planting lots of trees. Many insulation products use recycled materials, which helps reduce waste. Studies show good insulation can lower CO2 by up to 50%. You help fight climate change and make your home greener by choosing insulation.
Picking the right thermal insulation helps you use less energy. It keeps you comfortable and helps keep you healthy. You should think about some important things:
R-value shows how well it keeps heat in or out
Air and vapor permeability tells if air or water can pass through
Moisture tolerance means it can handle getting wet
Fire resistance shows if it can stop fire from spreading
Installation needs tell you how easy it is to put in
Cost and soundproofing help you decide what fits your budget and blocks noise
When you upgrade insulation, you get good results for a long time. You pay less for energy, feel better inside, and your home is worth more. You can also get money back with tax credits or rebates, which makes it easier to upgrade.
| Sector | Energy Savings | Carbon Reduction | Payback Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 10-45% | 10 billion tons | 6-12 months |
| Commercial | 7-9% | 360 million tons | 1 year |
| Industrial | $126 billion | 118 billion therms | 6 months |
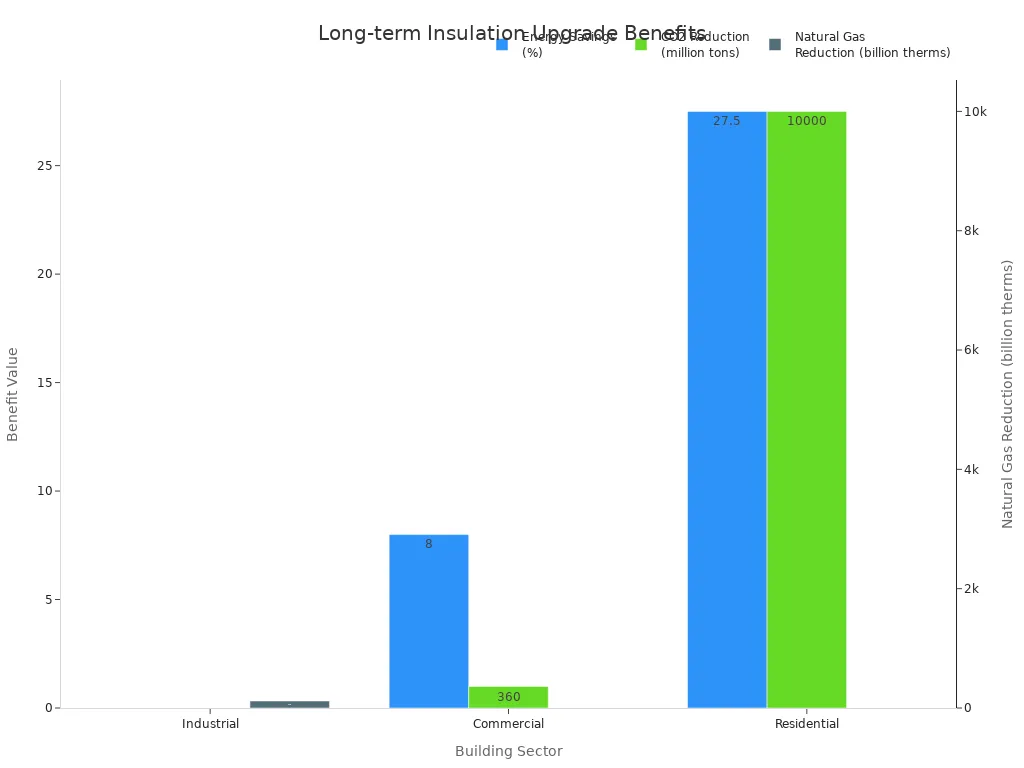
Tip: Upgrading thermal insulation makes your space safer, greener, and more comfortable for a long time.
Thermal insulation helps you control heat flow. You keep your home warm in winter and cool in summer. This saves energy and makes your space more comfortable.
You may feel drafts, cold spots, or see high energy bills. If your rooms change temperature quickly, you likely need better thermal insulation.
You can install some types of thermal insulation, like fiberglass batts or foam panels. Always follow safety tips. Wear gloves, a mask, and long sleeves.
Focus on attics, walls, and floors. These areas lose the most heat. Good thermal insulation in these spots gives you the best energy savings.
Yes! Many thermal insulation materials also block sound. You get a quieter home and less noise from outside.