Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-20 Origin: Site
Choosing the right packing material is important. It helps you get better insulation and sealing in tough places. Ceramic Fiber Insulation is special because it can handle high heat and hard jobs. Many industries use ceramic fiber packing:
Petrochemical plants use it for refining and distillation.
Power generation needs it for turbines and boilers.
Aerospace uses it for engine heat shields.
Automotive companies use it for exhaust and battery safety.
Chemical and metal plants like its strong resistance.
Homes and businesses put it in HVAC systems and stoves.
Ceramic fiber packing can take much more heat than fiberglass. This makes it good for very hot places like furnaces and power plants.
Fiberglass packing is simple to put in and costs less money. It works well for medium heat and helps block sound in homes and cars.
Ceramic fiber packing lasts longer and fights chemicals better. You must be careful with it because of dust and its higher price.
Pick your packing by looking at how hot your job gets. Think about chemicals, how long you need it to last, and your budget. This helps you get the safest and best results.
Always wear safety gear when you use either material. Follow your local rules for putting it in and throwing it away.
Fiberglass packing and ceramic fiber packing are made from different things. Fiberglass packing starts with things like silica sand, limestone, and soda ash. These get melted at high heat to make glass. The glass is spun or blown into fibers. Binders are put on the fibers. Then, they are shaped into mats, ropes, or fabrics. Sometimes, resins like polyester or epoxy are added. This makes the material stronger and easier to use.
Ceramic fiber packing is made in another way. It uses aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide. These minerals melt in a furnace. The melted mix turns into thin ceramic fibers by spinning or blowing. Workers gather the fibers into a soft pile. They shape it into blankets, boards, or ropes. Sometimes, binders are added and vacuum forming is used. This helps get the right shape and thickness. Ceramic fiber can handle much higher heat than fiberglass.
Tip: If you need insulation for very hot places, ceramic fiber insulation works better because of its special minerals.
You might wonder how these materials work in real life. Here are some things to think about:
Heat Resistance:
Fiberglass packing works up to medium heat. It breaks down if it gets too hot. Ceramic fiber packing can take much higher heat. It works up to 2300°F all the time and even more for short times. This makes ceramic fiber great for very hot places.
Durability and Strength:
Fiberglass is light and simple to put in. But it gets weaker over time, especially in hot spots. Ceramic fiber packing lasts longer and stays strong in tough places. You can see the strength difference in this table:
| Material/Form | Tensile Strength (lb/f) | Durability at High Heat |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber Tape | 58 | Excellent |
| Ceramic Fiber Braid | 110 - 150 | Excellent |
| Ceramic Fiber Twisted Rope | 75 - 100 | Excellent |
| Fiberglass (general) | Lower (not specified) | Degrades over time |
Thermal Conductivity:
Ceramic fiber packing lets less heat pass through than fiberglass. This means it insulates better. For example, ceramic fiber insulation can have a thermal conductivity as low as 0.10 - 0.25 W/(m·K) at 500°C. Fiberglass does not work as well at high heat.
Cost and Handling:
Fiberglass packing costs less and is easy to cut and put in. Ceramic fiber packing costs more and needs careful handling. The fibers can bother your skin and lungs.
Noise Reduction:
Fiberglass is good for blocking noise. This makes it useful in buildings and cars.
Forms and Flexibility:
Both materials come as ropes, tapes, and blankets. Fiberglass is easier to shape and install. Ceramic fiber is lighter and has lower thermal mass. This helps when you need fast temperature changes.
Note: If you need insulation for very hot or tough jobs, ceramic fiber packing is stronger and lasts longer. For easier jobs, fiberglass packing may be enough and saves money.
Fiberglass packing is made from glass fibers. These fibers are spun or woven together. The fibers are often packed loosely. This lets you squeeze them into small spaces. You can use this to fill gaps around pipes or equipment. When you press the fibers, they get denser. This makes the insulation stronger. The R-value per square inch goes up. But if you press too much, it gets thinner. This lowers the total R-value.
Fiberglass packing comes as ropes, tapes, or mats.
You can squeeze it to fit odd shapes or tight spots.
The fibers do not get damaged by most chemicals or water.
Fiberglass melts at a lower temperature than Ceramic Fiber Insulation, so it is not good for very hot places.
In firestop systems, fiberglass is often used with intumescent sealants or mineral wool. This helps keep the insulation in place and makes it better at stopping fire.
It is important to install fiberglass packing the right way. If you leave spaces, air can get through. This can make your energy bills go up and cause mold.
Tip: Always pack fiberglass insulation tightly so there are no spaces. Spaces can make your insulation work worse and lower fire safety.
Fiberglass packing is used in many industries. It is easy to use and works well. It is good for insulation and sealing where it does not get as hot as with Ceramic Fiber Insulation.
| Application Area | Common Use for Fiberglass Packing |
|---|---|
| Boilers & Furnaces | Sealing doors and access points |
| Ovens & Stoves | Insulating and sealing heat zones |
| Automotive | Gaskets for exhausts and engines |
| Industrial Equipment | Protecting from dust, leaks, and debris |
| Electrical Enclosures | Shielding components from chemicals |
Fiberglass rope is often used to seal doors on boilers, ovens, and wood stoves. In cars, it is used as a gasket in exhausts and engines. Factories use it to keep heat in and cold out. This helps their systems work better. Fiberglass packing also keeps dust and leaks away from equipment. Because it resists chemicals, it is good for electrical enclosures in tough places.
Note: If you need insulation for very hot or fire-rated jobs, you should think about Ceramic Fiber Insulation. For most regular sealing and insulation, fiberglass packing is strong and saves money.
Ceramic fiber insulation is used where it gets very hot. This material has alumina and silica, which are tough minerals. Workers melt these minerals and spin them into thin fibers. The fibers make a soft, light material with lots of tiny air pockets. These air pockets slow down heat, so less heat gets through.
Ceramic fiber insulation works well because of its special build:
The fibers make small spaces filled with air. Air does not move heat well.
Thinner fibers make smaller spaces, which stop heat better.
The fibers go in many directions. Heat has trouble moving through them.
The material is light and does not hold much heat. This lets you change temperatures fast.
You can use ceramic fiber insulation in places from 2000°F to 3000°F. Most types work up to 2300°F or more. This is much hotter than fiberglass or mineral wool. The chart below shows how ceramic fiber insulation stands up to other materials:
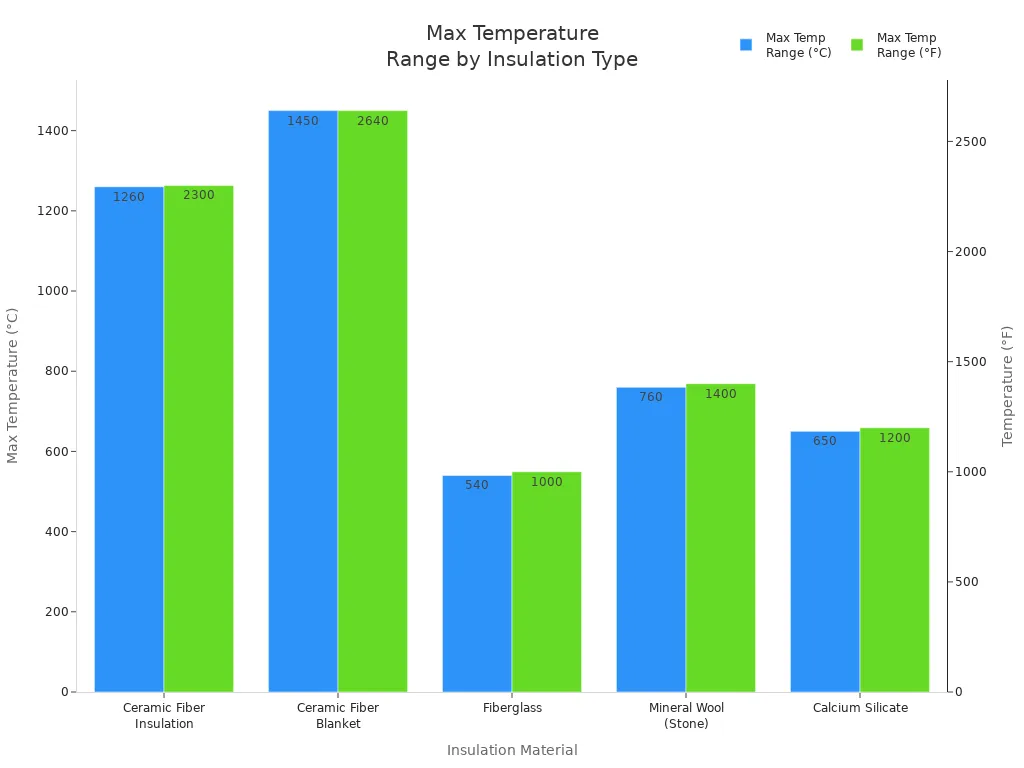
Ceramic fiber insulation comes in many shapes. You can pick the best one for your job. Here is a table that shows the main types and what they do:
| Form of Ceramic Fiber Insulation | Description |
|---|---|
| Blankets | Soft, no binder, easy to wrap around pipes or machines. Can have foil on the back for more protection. |
| Modules | Blocks made from folded blankets, used for lining furnaces and sealing gaps. |
| Macromodules | Big panels for quick setup in hot places. |
| Papers | Thin sheets for light insulation in small spaces. |
| Boards | Hard panels for strong insulation and support. |
| Bulk & Engineered Fibers | Loose fibers for filling odd shapes or making special parts. |
| Textiles (Cloth, Tape, Rope) | Woven items for flexible sealing and wrapping. |
You see ceramic fiber insulation in many jobs:
Power plants use it to cover turbines and super heater tubes.
Steel and foundry companies put it in blast furnaces and melting ovens.
Chemical plants use it for lining reformers and expansion joints.
Solar power systems use it to keep backup heaters warm.
It is used in kiln car insulation, furnace door seals, and pipe covers.
Car and airplane companies use it for exhausts and fire safety.
Ceramic fiber insulation gives strong heat resistance, low thermal conductivity, and is easy to use. You save energy and get better safety in hot jobs. The light weight makes it easy to put in, and you can pick blankets, boards, or loose fibers for your needs.
Tip: If you need insulation for places with very high heat, ceramic fiber insulation gives the best protection and works well.
Ceramic fiber products come in many types. You can get blankets, boards, modules, papers, and textiles like cloth and rope. Each type does something different. Blankets are soft and bend easily for insulation. Boards are hard and give strong support. Modules are good for lining kilns. Papers help seal things and make gaskets. Textiles are used to wrap or filter.
Ceramic fiber products are special because they work in very hot places. You can use them where it gets up to 1600°C. They do not break down from chemicals or air. This means they last longer in tough places. They also stay in place when machines shake. New micro-nanofiber technology makes them lighter and better at stopping heat.
Here are some main benefits:
They are light, so shipping and putting them in costs less.
They do not let much heat pass through, so you save energy.
You can bend or shape them to fit many jobs.
They are strong and do not wear out fast from shaking or heat.
You can put them in quickly and fix them easily.
They spread heat evenly, so you get better control and quality.
Tip: You can use ceramic fiber products with other things, like aerogels, to make insulation even better.
Ceramic fiber products have some problems you should know. When you touch them, they make dust. This dust can bother your lungs. You need to wear safety gear when you put them in. They are not as strong as some other materials. If you hit or rub them too much, they can break. Making these fibers costs more because it needs pure stuff and special steps.
The table below shows the main problems and what they mean:
| Limitation | Explanation | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Stability | Fibers get weaker after lots of heat or heating and cooling again and again. | You need more repairs, spend more money, and may have downtime. |
| Susceptibility to Erosion | Fast air or rough bits can wear away the fibers. | You lose insulation, heat escapes, and machines can get hurt. |
| Peeling Off Due to Air Flow | Layers can come off if strong air blows on them. | Insulation is not even, some spots get too hot, and it works less well. |
| Dust Generation | Handling makes dust that can bother your breathing. | You must use safety steps when putting it in. |
| Lower Mechanical Strength | Fibers break easily if you hit or rub them. | You cannot use them where things get hit a lot. |
| Higher Production Costs | Making them needs pure stuff and hard steps. | You pay more at first. |
| Contamination Issues | Fibers can get dirty from other stuff or the air. | Insulation does not work as well and machines may not last long. |
Note: If you need insulation where things move or get hit a lot, you might want to try something else.
When you pick between fiberglass packing and ceramic fiber packing, you need to think about a few things. Each material works best in certain jobs. You should make sure your choice fits your needs for heat, place, and price.
Temperature Range:
If your job needs insulation for very high heat, ceramic fiber packing is better. It can take much more heat than fiberglass. Fiberglass works up to about 500°F. Ceramic fiber insulation can handle up to 2300°F or even more for short times.
Environment:
Think about where you will use the packing. If you need strong resistance to chemicals or lots of water, ceramic fiber packing is stronger. It stands up to acids, alkalis, and even melted metal. Fiberglass also resists many chemicals but may not last as long in tough or wet places.
Sound Absorption:
Both materials help block noise. Fiberglass is very good for stopping sound in buildings and cars. Ceramic fiber also blocks noise but works best in hot, busy places.
Durability and Lifespan:
Ceramic fiber packing lasts longer in hard, hot jobs. It keeps its shape and strength after many heating and cooling cycles. Fiberglass may get weaker or lose power over time, especially with shaking or water.
Cost:
Fiberglass packing usually costs less. It is a good pick if you have a small budget and do not need high heat resistance. Ceramic fiber packing costs more at first but saves money later because it lasts longer and needs less fixing.
Safety and Handling:
Both materials can bother your skin and lungs. You should always wear gloves and a mask when you touch them. Ceramic fiber insulation can make more dust, so you need to be extra careful and follow local rules when you throw it away.
Chemical Compatibility:
Always check if the packing can resist the chemicals in your system. This helps stop damage and keeps your equipment safe.
Tip: Always match the packing to your system’s pressure and temperature ratings. This helps stop leaks and keeps your equipment safe.
Here is a table to help you compare fiberglass and ceramic fiber packing:
| Feature | Fiberglass Packing | Ceramic Fiber Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 500°F (260°C) | Up to 2300°F (1260°C) or higher |
| Heat Resistance | Good for low to moderate heat | Excellent for extreme heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but less than ceramic fiber | Excellent, resists acids, alkalis, molten metals |
| Sound Absorption | Excellent | Very good |
| Durability | Can degrade with moisture, vibration, or over time | Very durable, long lifespan in harsh conditions |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, but saves money over time |
| Ease of Installation | Easy to cut, shape, and install | Lightweight, flexible, but needs careful handling |
| Safety | Noncombustible, but can irritate skin and lungs; needs PPE | Non-toxic, but fiber dust can irritate; needs PPE and proper disposal |
| Best Use | Buildings, vehicles, moderate heat, soundproofing | Furnaces, kilns, power plants, high temperature processing |
Pick fiberglass packing if:
You want a cheaper solution for lower heat.
You need good sound blocking in homes, offices, or cars.
Your place is not very tough or full of strong chemicals.
Pick ceramic fiber packing if:
You need insulation for very hot jobs like furnaces or power plants.
Your job has strong chemicals or very high heat.
You want something that lasts a long time in hard places.
Note: Always wear safety gear when you put in or take out any packing. Follow local safety and disposal rules, especially with ceramic fiber products.
By thinking about these things, you can choose the best packing for your job. The right choice helps you save money, protect your equipment, and keep your workplace safe.
It is important to know how fiberglass packing and Ceramic Fiber Insulation are different. The table below shows how they work in hard jobs:
| Property | Fiberglass Packing (Type E) | Ceramic Fiber Packing (Twisted Rope) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Works up to about 800°F | Handles over 2552°F |
| Mechanical Strength | Stays strong at medium heat | Very strong at very high heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Can be hurt by bases | Stands up to acids and alkalis |
| Typical Use | Used for medium insulation | Used for sealing in hot places |
Knowing these facts helps you pick the best insulation for your job. You can use this checklist to help you decide:
Make sure the material works for your heat needs.
Think about what chemicals and how long it must last.
Compare prices and how long each will work.
See if you can get the product nearby and get help if needed.
Tip: Always pick packing that fits your system’s heat and place. This keeps things safe and working well.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation has alumina and silica minerals. These minerals melt and spin into thin fibers. The fibers make a light material that blocks heat well. You find it as blankets, boards, and ropes.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation works in much hotter places than fiberglass. You can use it where it gets up to 2300°F. Fiberglass is best for places under 500°F. Pick ceramic fiber for furnaces and kilns.
You need to wear gloves and a mask. The fibers can bother your skin and lungs. Always follow safety rules. Throw away waste the way your town says.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation is used in power plants and chemical factories. Metal foundries also use it. It works for furnace linings, pipe covers, and fire protection. You see it in cars and airplanes too.
Yes, you can cut and shape Ceramic Fiber Insulation with simple tools. It bends and fits many spaces. Be gentle when you handle it so you do not make dust.